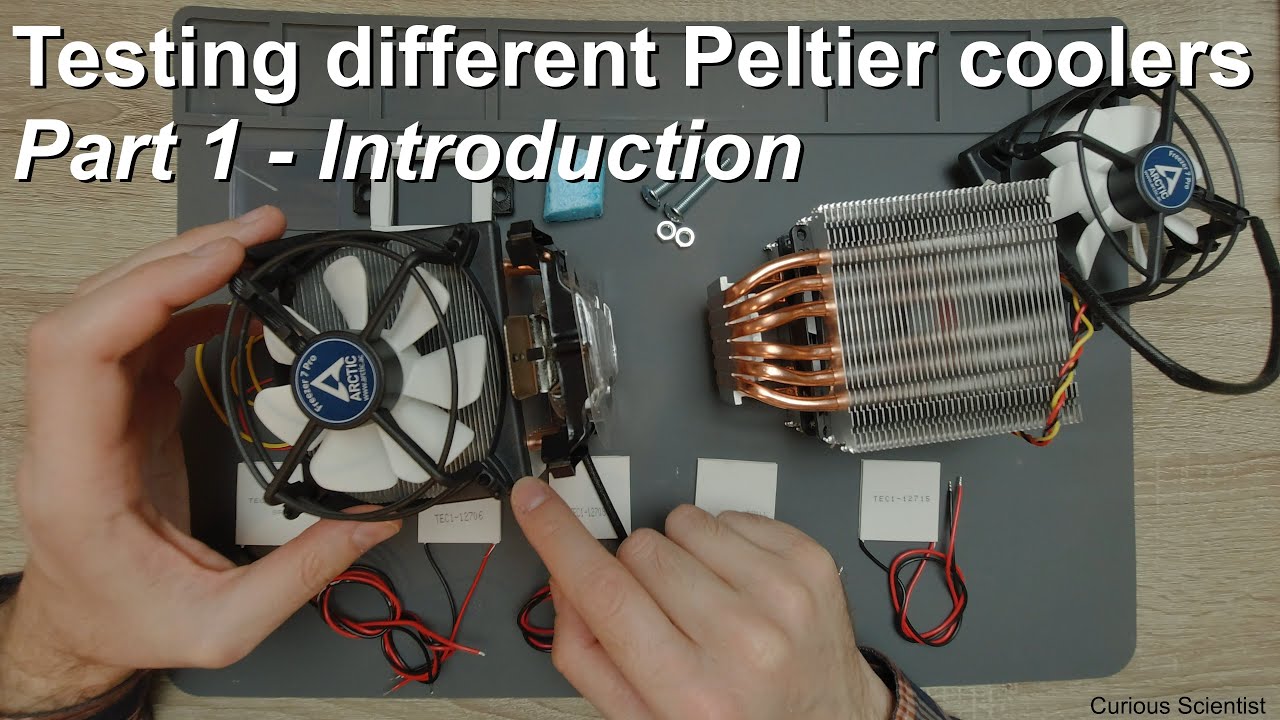
Testing and comparing different Peltier coolers Part 1 Introduction
Thermoelectric cooling uses the Peltier effect to create a heat flux at the junction of two different types of materials. A Peltier cooler, heater, or thermoelectric heat pump is a solid-state active heat pump which transfers heat from one side of the device to the other, with consumption of electrical energy, depending on the direction of the current.. Such an instrument is also called a.

Powerful Cooler Box DIY Peltier Freezer YouTube
Peltier effect, the cooling of one junction and the heating of the other when electric current is maintained in a circuit of material consisting of two dissimilar conductors; the effect is even stronger in circuits containing dissimilar semiconductors. In a circuit consisting of a battery joined by two pieces of copper wire to a length of bismuth wire, a temperature rise occurs at the junction.
Peltier cpu cooler Pneumatisk transport med vakuum
In 1834, a scientist called Peltier discovered the inverse of the Seebeck effect, now known as the "Peltier effect": He found that if you take a thermocouple and apply a voltage, this causes a temperature difference between the junctions. This results in a small heat pump, later referred to as also known as a thermo-electric cooler (TEC) .

Peltier Peltier Air Cooler
Thermoelectric devices are semiconductor heat or refrigeration units which use the Peltier effect to create a heat flux between the two surfaces of the modul.

DIY Peltier Beverage Cooler Box 9 Steps (with Pictures) Instructables
The Peltier effect is the basis for many modern day TE refrigeration devices and the Seebeck effect is the basis for TE power generation devices (see Thermoelectric Devices: Refrigeration and Power Generations With No Moving Parts).The versatility of TE materials is illustrated in Fig. 3 which shows a diagram of a thermoelectric couple composed of an n-type (negative thermopower and electron.

60w Semiconductor Thermoelectric Peltier Refrigeration Cooling Heatsink
Upon application of a direct current (DC) power source, these devices generate a cooling action, countered by a generation of heat on the opposite side of the device. EIC's Thermoelectric Air Conditioners operate on this principle so there is no compressor and no expensive, ozone-depleting CFC's. EIC's Peltier assemblies use.
The Peltier effect a ‘cool technology’ for thermal desorption
Named after the French physicist Jean Charles Athanase Peltier, who discovered the Peltier effect, these devices operate on an entirely different principle than conventional cooling systems. The Peltier Effect: Principle and Functioning. At its core, a Peltier device employs a phenomenon known as the Peltier effect. This is a thermo-electric.

Homemade Peltier Cooler / Fridge With Temperature Controller DIY 6
The Peltier effect is also referred to as "solid-state refrigeration" because it uses solid-state materials (such as semiconductors) to achieve cooling, rather than traditional methods like compression and evaporation of refrigerants.This makes it a more efficient and eco-friendly alternative to traditional refrigeration methods.

Solar powered thermoelectric peltier cooler freezing test YouTube
Today we will be doing some "science experiments" with a popular thermoelectric cooling device, the TEC1-12706 Peltier Module. We will also learn about the P.

(PDF) Peltier cooling at molecular scale
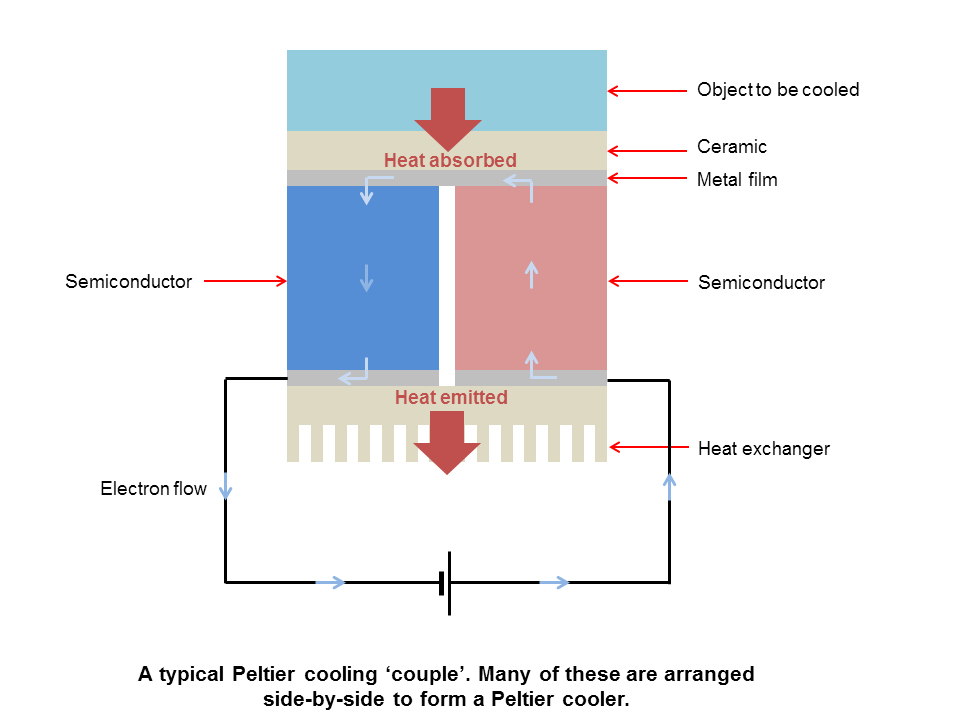
Thermoelectric cooling takes advantage of the Peltier effect, which is observed as heat being either absorbed or emitted between the junctions of two dissimilar conductors when a current is passed. A thermoelectric module comprising a Peltier element sandwiched between two ceramic plates of high thermal conductivity, with a power source, is.

WiMas DIY Peltier Cooler Kit 12V Semiconductor
Observing the Peltier effect, e.g. cooling/heating at material junctions due to current flow, in organic thermoelectric films remains a challenge due the inherent properties of these materials.
1X(Thermoelectric Peltier Refrigeration Cooling System Kit Cooler
How Peltier cooling works. The Peltier effect is the heat exchange that results when electricity is passed across a junction of two conductors, and is a close relative of the Seebeck effect (effectively the same phenomenon in reverse, used in thermocouples used to measure temperature), and the Thomson effect (generation of electricity along a conductor with a temperature gradient).
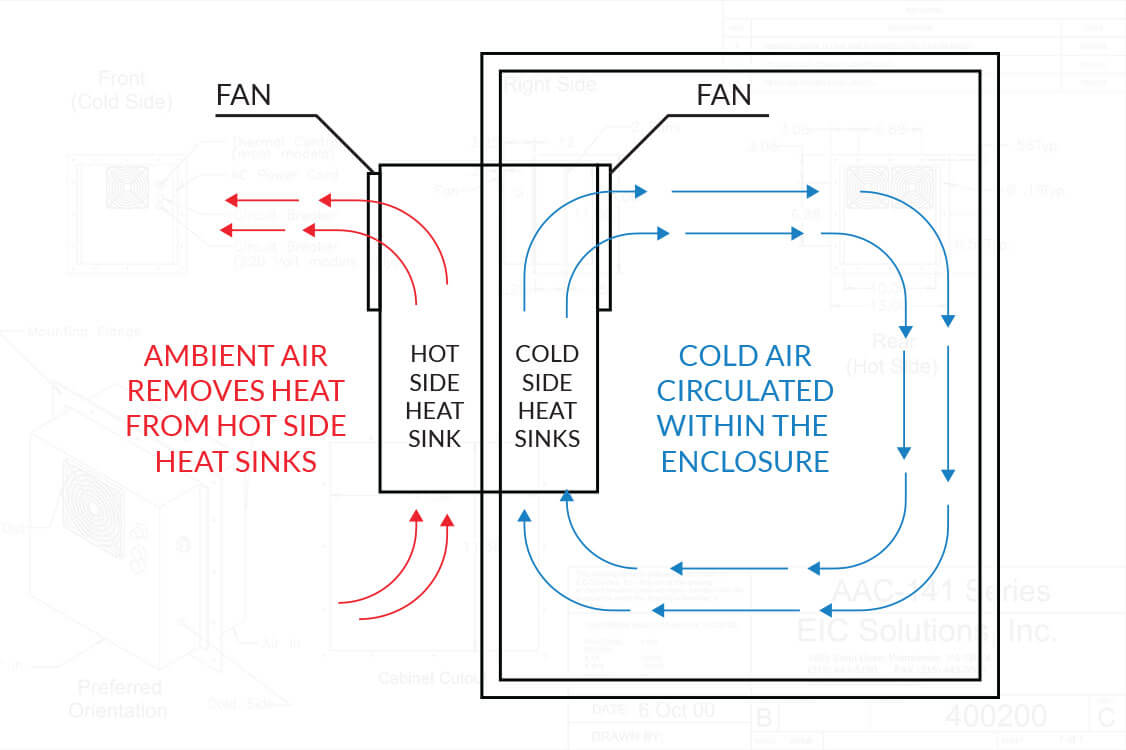
How Peltier Cooling Works EIC Solutions
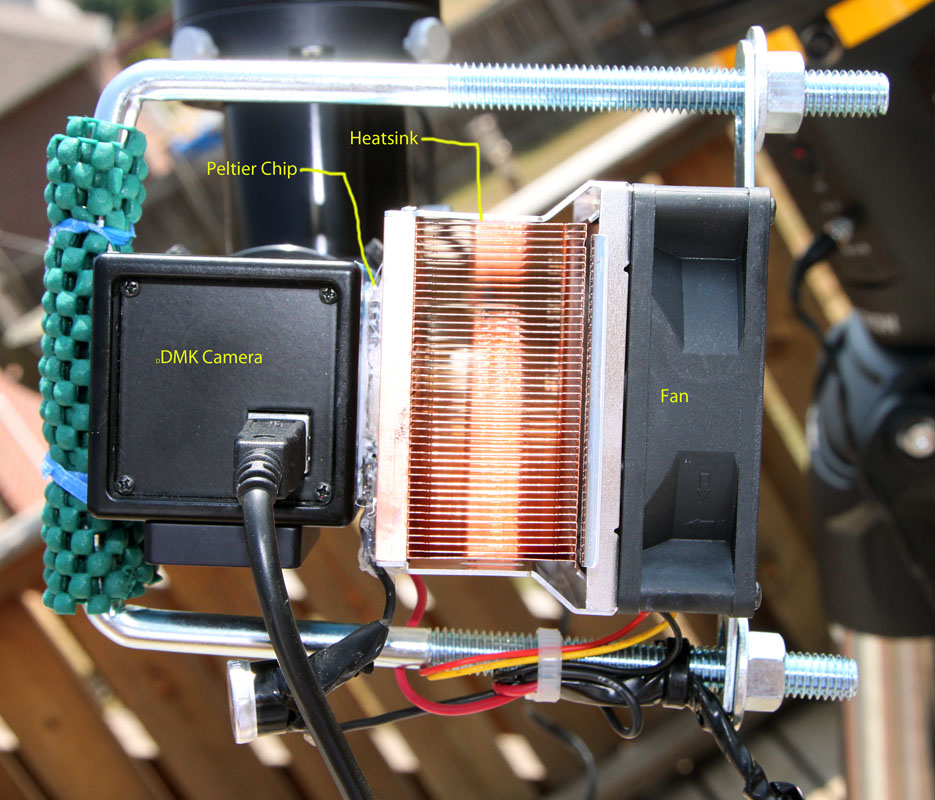
Peltier Effect & Thermoelectric Coolers (TECs) TECs are solid state Peltier devices that, once a DC current is applied, will transfer heat from one side to the other. This means that one side of the device will produce cold while the other side produces heat. The heated side is often attached to a heat sink so that the device can be used for.

12V 72W Thermoelectric Peltier Refrigeration Cooling System Kit Cooler
June 13, 2019. A Peltier cooler is a device that uses the Peltier effect to produce cooling or heating. The Peltier effect is defined as the emission or absorption of heat under an electrical bias at a junction between two conductors. When an electric current flows through the junction, heating or cooling can be achieved.

Water Cooler Using peltier module How to make YouTube
The Peltier Effect. Thermoelectric coolers operate according to the Peltier effect. The effect creates a temperature difference by transferring heat between two electrical junctions. A voltage is applied across joined conductors to create an electric current. When the current flows through the junctions of the two conductors, heat is removed at.

Peltier Effect Cooling Experiments with a Peltier Cooler Device YouTube
The thermoelectric effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice versa via a thermocouple. A thermoelectric device creates a voltage when there is a different temperature on each side. Conversely, when a voltage is applied to it, heat is transferred from one side to the other, creating a temperature difference. At the atomic scale, an applied.